You’ve seen it in the headlines, you’ve heard about it through the grapevine, now you want to know what blockchain is exactly. Let’s run you through the basics, what it is, how it works, the history, and why it is such a universal tool. Here’s the ultimate guide to the distributed ledger technology, a simple introduction to what is blockchain technology.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
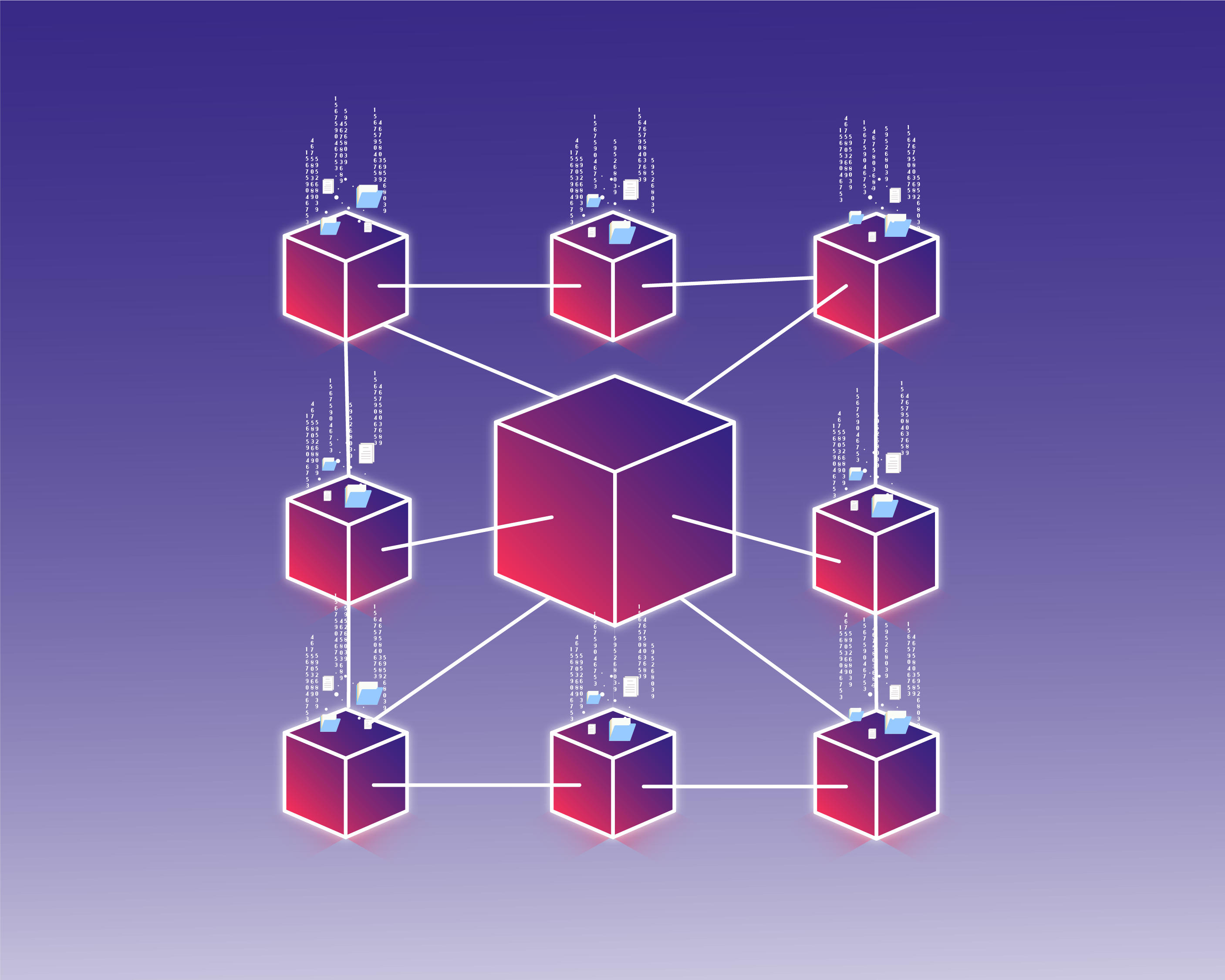
Let’s start with the basics. Blockchain technology can be likened to a public distributed ledger, meaning that all transactions are entered into the ledger in real time, and made available for all parties to see. This information is transparent as well as immutable, meaning that no one can go and make changes to previous entries. Each piece of data entered into the blockchain is stored in blocks, and these blocks make up a chain of information that anyone anywhere can access. As no single entity or server controls the activity on the blockchain, it is considered to be a decentralized network.
Who Controls Blockchain?
The beauty of and power behind blockchain technology is that no single entity controls it, making it completely autonomous. A blockchain network is made up of various nodes (computers) that work together to confirm that the information being added is accurate. These nodes constantly store and share the information on the network, ensuring that it is constantly up to date.
As no one is in control of the network, this makes blockchain technology much more secure when compared to centralized systems.
How Does Blockchain Work?
When looking at blockchain from a business or cryptocurrency perspective, the concept remains the same. The technology is able to programme, record and track anything of value in a trustless and transparent manner. Each piece of information is stored in a block, and then verified by a certain number of nodes in the system. This decentralized approach to verifying (and storing data) creates a level of trust, ensuring that no information on any of the blocks can be tampered with.
On a more technical level, each block contains the hash (fingerprint) of the block, the hash of the previous block and the data. The data could be a financial record, land title, or a transaction.
Let’s look at Bitcoin’s blockchain for example, each block includes the details of the sender, the receiver, and how much Bitcoin was sent. When a new block is created, each node on the system verifies that the transaction is genuine, and when everyone is happy that it hasn’t been tampered with, it is added to the blockchain.
This system of nodes and the hash train is what makes blockchain so secure.
A Brief History Of Blockchain Technology
When looking to understand what blockchain is, or anything for that matter, it always serves well to take a look at its history. You might be surprised to find out that blockchain technology was first introduced in 1991. Two developers working on a digital document filing system created a protocol where each document was time stamped. Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta headed the project and built the initial code. However, this didn’t catch on and the patent expired in 2004.
That same year, computer scientist Hal Finney created a system where peer-to-peer exchanges of a token could be conducted, leveraging the initial blockchain concept and solving the double spending problem. This system is widely considered to be an early prototype of cryptocurrencies as we know them today.
It wasn’t until 2009 when Satoshi Nakamoto released a whitepaper outlining a digital money system known as Bitcoin that blockchain solidified its existence. Bitcoin’s peer-to-peer exchange of value is based on blockchain technology, which has been widely adopted by many industries since. Many companies are now incorporating the technology into their internal and external operations, saving them considerable time and money.
What Is The Connection Between Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain?
As we touched on in the previous chapter, the first cryptocurrency to come into existence brought blockchain technology to light. All cryptocurrencies use blockchain technology to create, share and verify transactions. As there is no single entity in control, all transactions are conducted peer-to-peer and verified by other participants on the network. All transactions are then stored in a public ledger, for anyone to see. Harnessing the power of blockchain, cryptocurrency transactions can function 24/7 completely autonomously and securely on the network.
What Are The Advantages Of Blockchain Technology?
While it’s been over a decade since the technology first entered the scene, blockchain has seen widespread adoption in the more recent years. Now, big companies from Walmart, to Barclays, to Nestle and even the retail sector are adopting blockchain into their companies to their, or their customers, benefit. Listed below are just some of the many advantages to blockchain technology:
- Reliable and trustless value and data transmission
- Peer-to-peer, requiring no middleman
- Cheaper and faster money transfers, both locally and globally
- Capable of onboarding smart contracts
The Wonderful World Of Possibilities With Blockchain
As we’ve highlighted in this ultimate guide to the distributed ledger technology, blockchain can be used for many different purposes, in many different industries. Blockchain technology has not only revolutionised how we share data, but also how we transact value.
The power behind the nascent technology is endless, and is widely being adopted across the globe to the benefit of consumers, businesses, and people alike. When uncovering this simple introduction to blockchain technology, it’s a lot less intimidating than it sounds.
_________________________________________________________
Oobit Technologies Pte, 50 Raffles Place #37-00 Singapore Land Tower, Singapore (048623). is a company registered in Singapore (no:201716443G), that has been approved as Appointed Representative of Oobit Technologies OÜ, Harju maakond, Tallinn, Lasnamäe linnaosa, Väike-Paala tn 2, 11415, (no: 14852617 ). Which is authorized and regulated by the FIU (no: FVR001421 and FRK001304).